How to Climb Stairs Part 1: Onward and Upward
Few of us, wheelchair users excepted, pass a day without climbing steps or stairs. Students often ask if posture has any bearing on how best to do this—and the answer is yes! Our approach to pain-free, healthy posture works precisely because it helps you with all your daily activities. This blog post is the first of several containing introductory tips for using steps and stairs. We will focus here on how to power yourself upward.
Steps and stairs—the benefits
If you are looking to maintain or improve your cardio fitness and lower body strength, climbing steps and stairs will check that box. For example, this could be opting for the stairs rather than the elevator at work.

Choosing to take the stairs over the elevator is an easy way to build movement breaks into your day. Pexels
Or, if you have a suitable baseline fitness, you can also use steps, stairs, or gym machines, to up the challenge in your training sessions.

Gokhale Method teacher Eric Fernandez being put through his paces on a step machine.
If you have mobility issues, perhaps due to joint injury, degeneration, or poor balance, using stairs could be something you need to take, literally, one small step at a time, and possibly with the help of a healthcare professional. However, once steps and stairs are appropriate for you, then, whether you are at the level of post-op rehab, or athletic training, the healthy postural form taught by the Gokhale Method® will make your efforts safer, encourage healing rather than damage, and make each step you take more efficient and powerful.
Safety first
Whatever your fitness and mobility level, first check that you can use steps and stairs safely:
- Use a handrail if that’s right for you
- Ensure good lighting in the area
- Watch out for wet, slippery, or unsound surfaces such a torn carpet or loose tiles
- Watch out for untied shoelaces, trailing clothing, and other trip hazards
- Wear well-fitting, non-slip shoes
Start with your stance
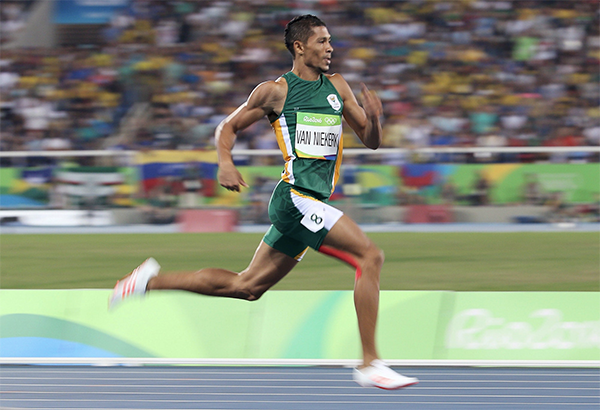
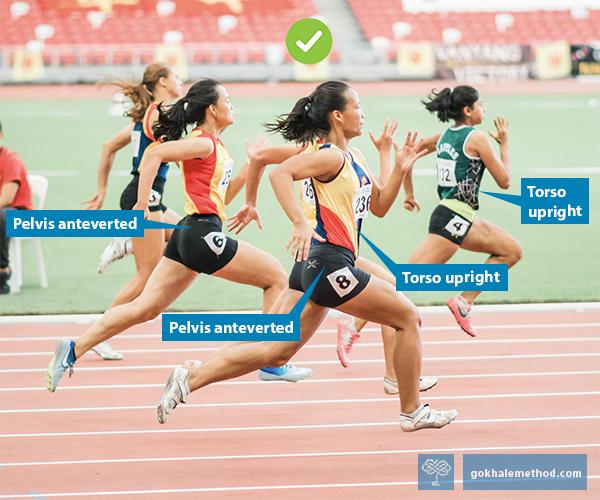
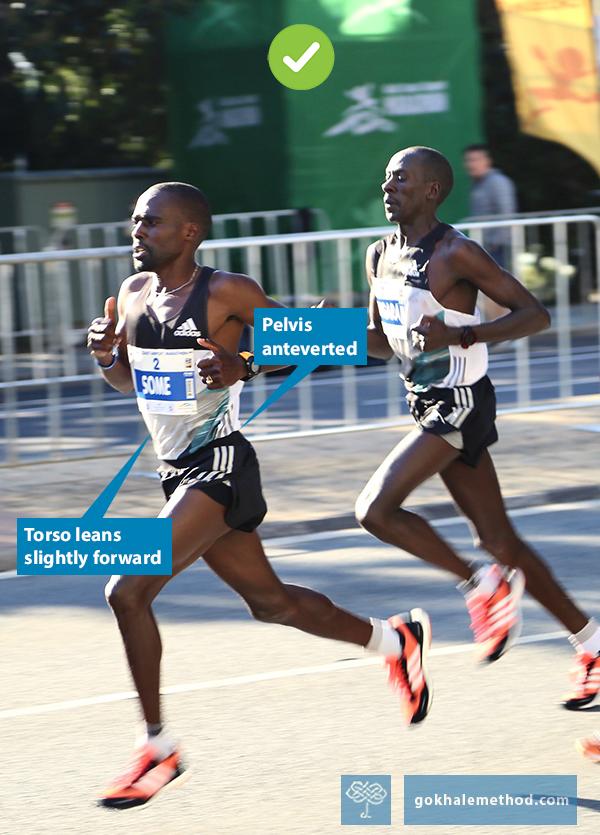
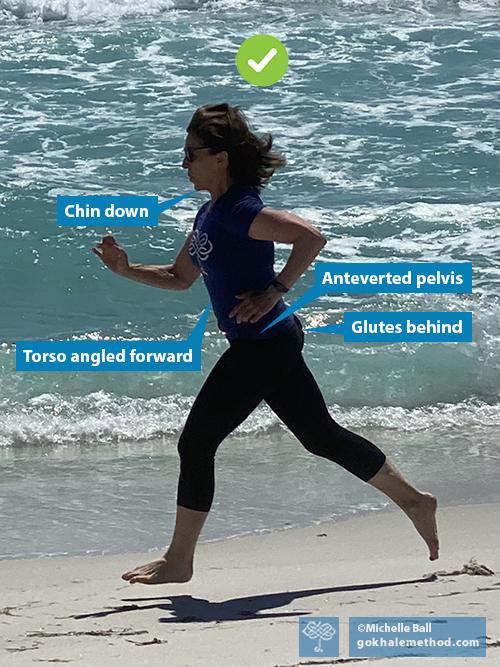
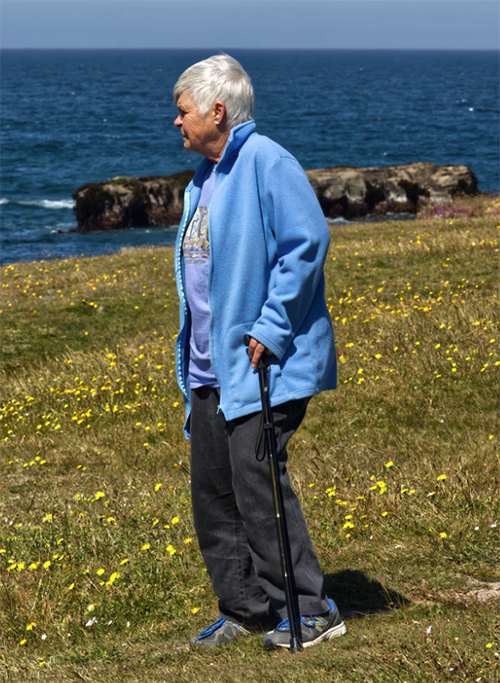
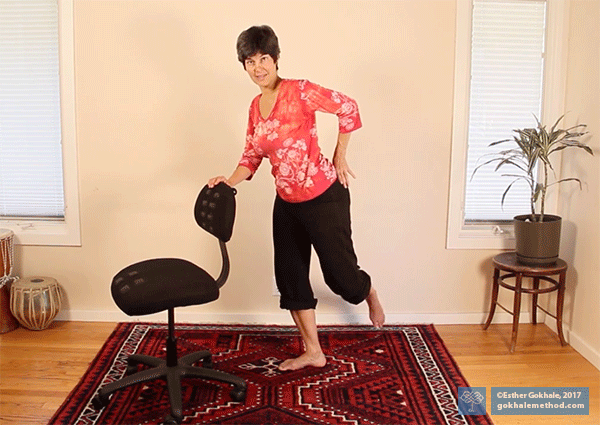
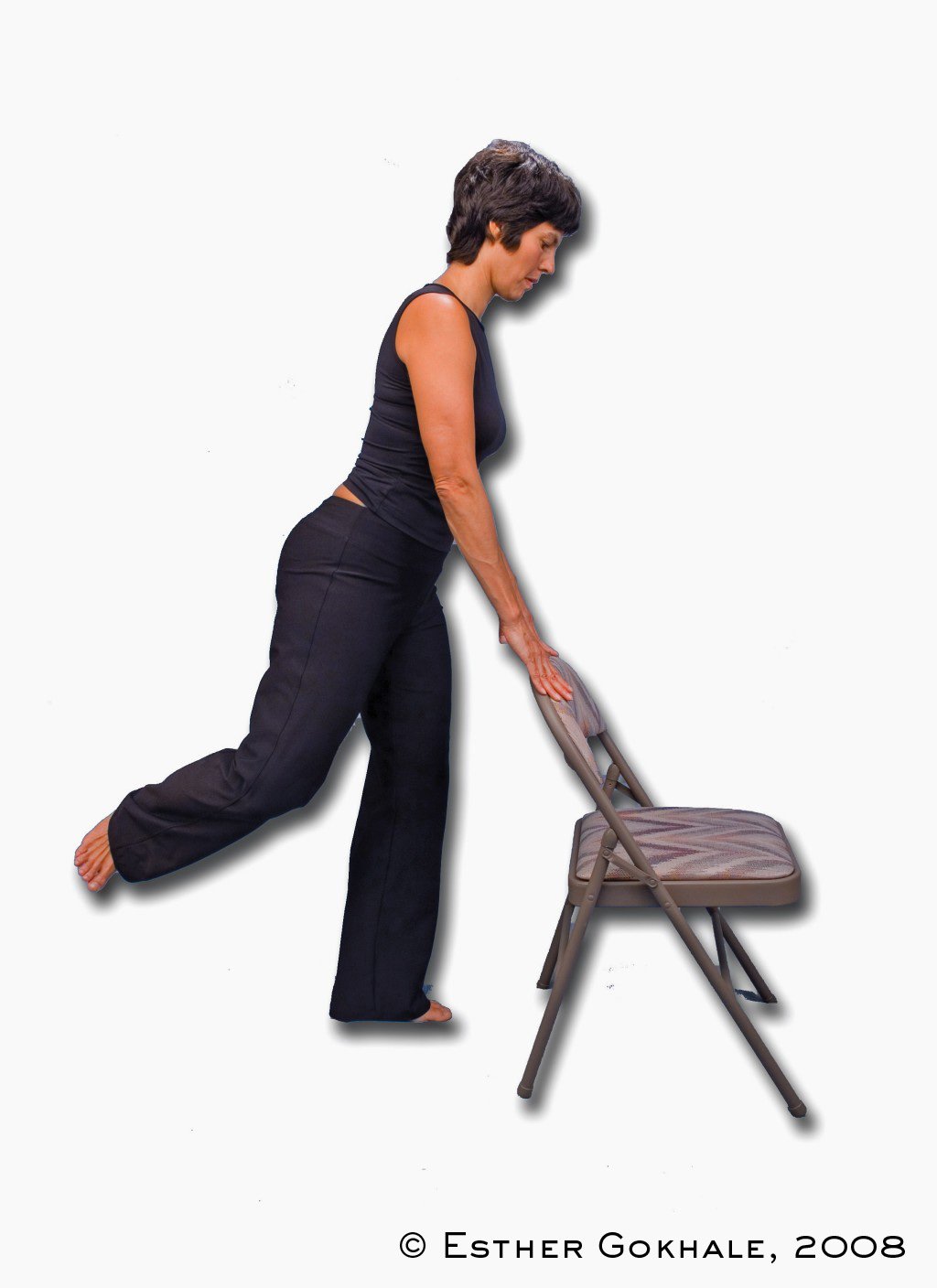
Angling your body forward slightly will be of immediate advantage. It will put your behind behind you, placing your glutes in a position of mechanical advantage where they can work optimally. The glutes are an important part of the posterior chain, that is, muscles in the back of the body, which need to play a prominent role in powering you forward.
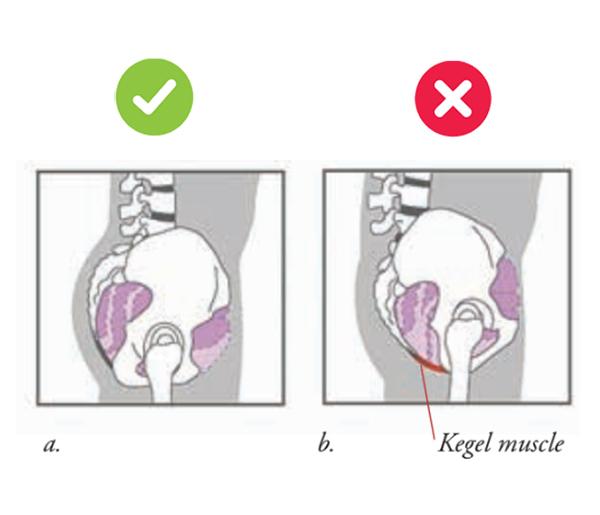
The body wants to angle forward in line with the back leg when walking up steps. ✅
Most people overly rely on pulling up their body weight with the anterior chain when they climb. This overuses the major hip flexor (psoas), and thigh muscles (quads). It is a pattern that usually arises because the pelvis is tucked, sending the “behind” underneath. With the pelvis tucked, the glutes are unavailable to contribute the forward propulsion that makes climbing easier.

Climbing steps with a tucked pelvis disadvantage the posterior chain muscles that do this job best.
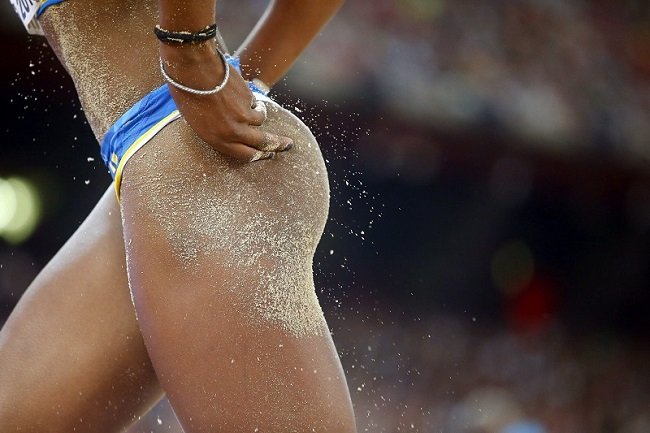
Squeeze those glutes for both stability and lift
As you stand on one leg and prepare to step up, adopt your forward stance and contract the glutes of that standing leg strongly. Gluteus medius will stabilize your leg and pelvis and help maintain your balance, while gluteus maximus will propel you forward and up to the next step.
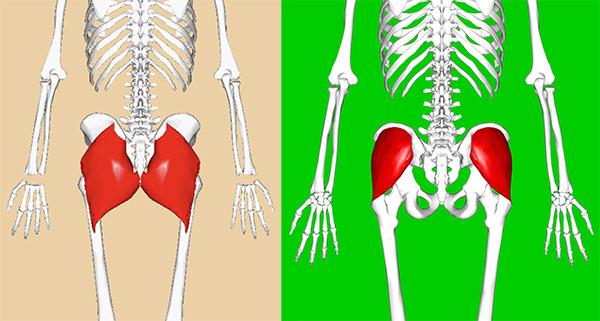
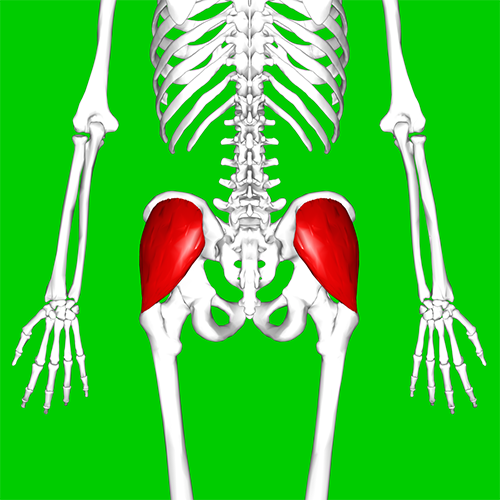
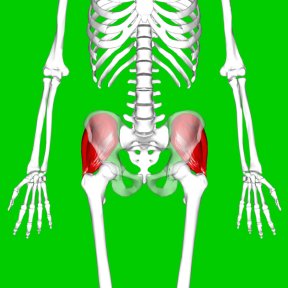
Knowing where your buttock muscles are situated can help you visualize them working: gluteus maximus (left) and, underneath it, gluteus medius (right).
The gluteus maximus is the largest and most superficial of the buttock muscles, and pulls your leg back. When one leg is fixed on the ground, as during walking or climbing steps, its muscular contraction will propel the body forward. The gluteus medius is closer to the hip joint, higher, and further out to the side, where it helps in maintaining balance as well as adding momentum.

Notice the glutes of the supporting leg actively contracting.
In addition to climbing stairs becoming easier, contracting your glutes has the additional advantage of giving you a more athletic appearance by toning and lifting your buttock muscles.
Work those calves and spare your knees
Lower down your posterior chain, your calves and feet are designed to do the job of propelling you upward. When the calf muscles of your standing leg contract, they lift your heel, driving your forefoot against the ground and your body up. Without the calves providing propulsion, too much heavy lifting will be relegated to your quads, which is likely to overload your knee joint.
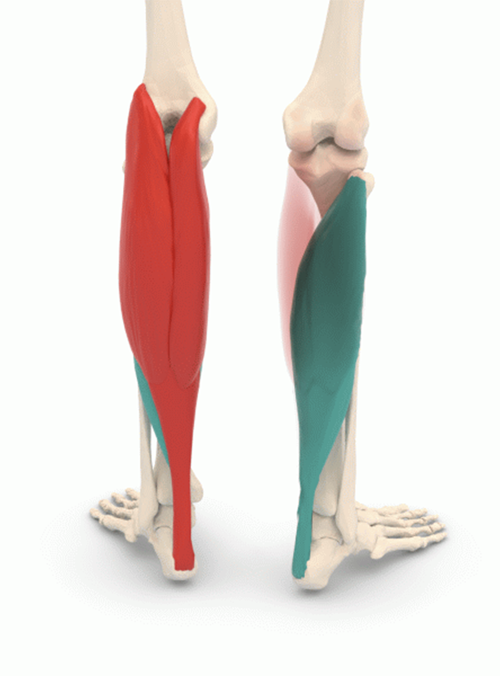
Most people are aware of their more visible calf muscle, gastrocnemius (in red); underneath it lies the deeper soleus (in green). They both contract to point the forefoot down, driving the heel and leg upward when the front of the foot is on the ground. Wikimedia
Using your calves will mean that your feet and ankle joints also get healthy work and movement. Often people climb stairs with their ankles fixed, having become accustomed to walking on flat urban surfaces—little wonder this joint becomes stiff, weak, and injury-prone. Climbing stairs with good postural form will lend your ankles much-needed mobility, and bring a welcome boost to the circulation in your lower limbs.
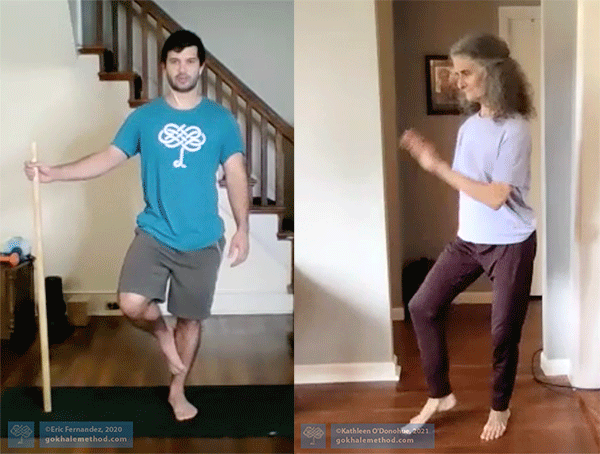
This slo-mo video shows the calf muscles of the rear leg contracting during the step up.
If you are not sure if you are activating your glutes as well as you might, you can find instructions in my book, 8 Steps to a Pain-Free Back, or sign up for my Free Online Workshop, Wake up Your Glutes: They Snooze, You Lose, on January 12, 1:30 pm PT.
If you would like more nuanced guidance on how to navigate steps and stairs, or on refining your glute squeeze, consider scheduling an Initial Consultation, online or in person, with a Gokhale Method teacher.
If you would like to find out more about how the Gokhale Method can help support you, sign up to join one of our upcoming FREE Online Workshops. . .