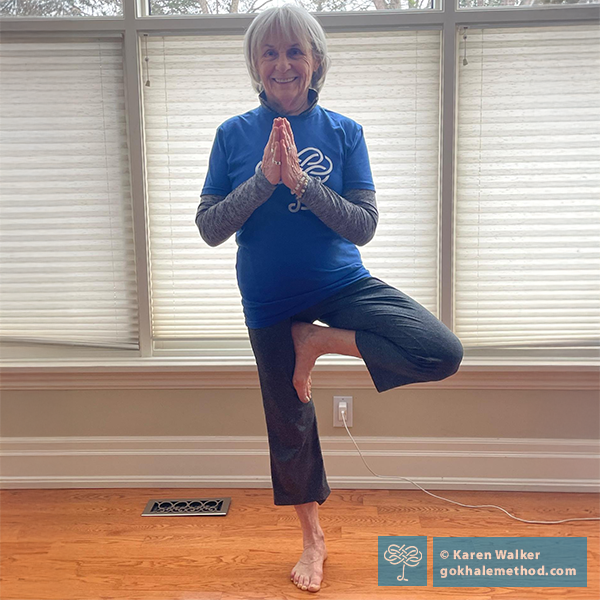
Several years ago, I was struggling with sleep apnea, knee pain, and chronic neck pain from an old diving injury—all despite my committed yoga practice. Something was missing. When I found the Gokhale Method®, I experienced a profound shift. My pain reduced. My stamina increased. I felt calmer, more confident, more capable in my body.
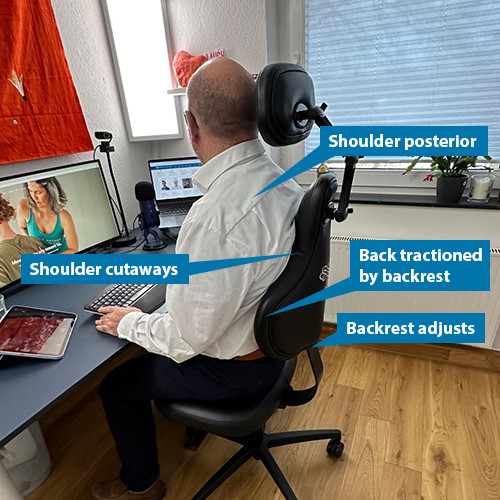
Is Your Chair Setting You Up for Back Problems?
There’s no doubt that dysfunction abounds when it comes to sitting. Most of us spend many hours on poorly designed chairs, in poor posture. As many people know all too well, poor sitting habits can definitely set you up for chronic back pain and tension.
The good news? With just a little time and awareness, we can learn to sit well. There is real beauty and functionality in sitting done skilfully! When you do, sitting becomes not only comfortable, but also healthful and therapeutic.
Tai Chi, Qigong, and Tucking the Pelvis
Our teachers often field questions about tucking the pelvis for Tai Chi and Qigong. It is frequently perceived that Tai Chi recommends tucking the pelvis as part of a baseline stance, purportedly to facilitate “the Qi to flow unimpeded.” It’s a central tenet in Gokhale Method® philosophy that the baseline pelvic position be anteverted, and that tucking the pelvis is a “wrong turn” Western society took about a century ago (think flapper posture). So students who encounter a seemingly exactly opposite guideline or model in Tai Chi are understandably confused.
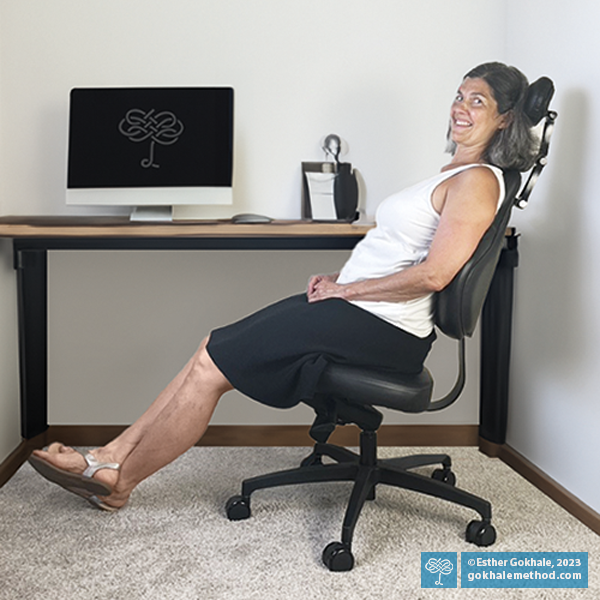
Recline and Relax, Executive-style!
Over the years, I have often shown students with recliners that they can get a compression-relieving stretch in their lower back as the backrest slides away from the seat (assuming the mechanism is designed advantageously). This is something you might like to try out for yourself.
Wake Up Your Glutes, They Snooze, You Lose
In surveys of what people find physically attractive in a partner, a shapely butt is often highly rated. Perhaps it’s no surprise, but if you want, there are even apps to help! So, are good-looking glutes all about sex appeal and filling out our clothing in a flattering fashion? While these concerns may be valid, it is also true that well-toned glutes have many other, profound, but less widely recognized attributes.
This blog post takes a look at the bigger picture of glute function. You may be surprised to find out just how much your glutes can contribute to healthy posture and a pain-free body.
How to Swim with Healthy Posture: Breaststroke
Vacation time is in full swing in the northern hemisphere. For many of us, being beachside or poolside gets us yearning for a dip, a splash, and a swim. And I’m guessing that many of us have been mesmerized and inspired by watching the Olympic pool athletes in action.
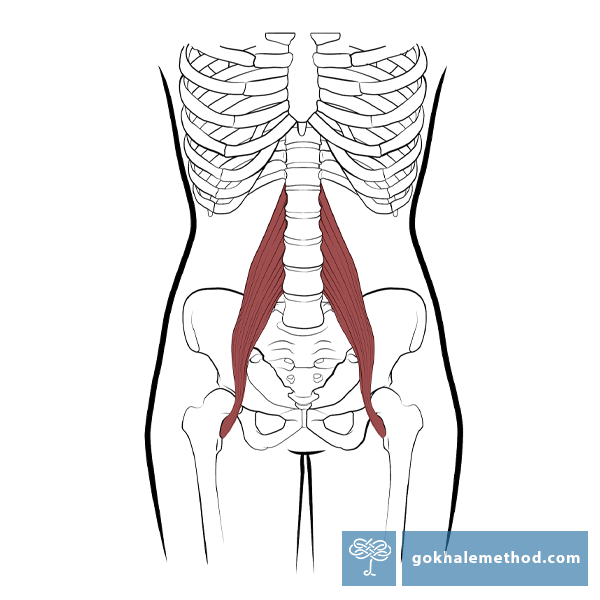
How to Fix a Tight Psoas
When students first meet with a Gokhale Method® teacher they are sometimes surprised to learn that one of the reasons for their back pain is a tight psoas muscle. What does this little-known muscle, embedded deep within our bodies, have to do with back pain? And what do we need to do to have it recede in the background and leave our backs alone?
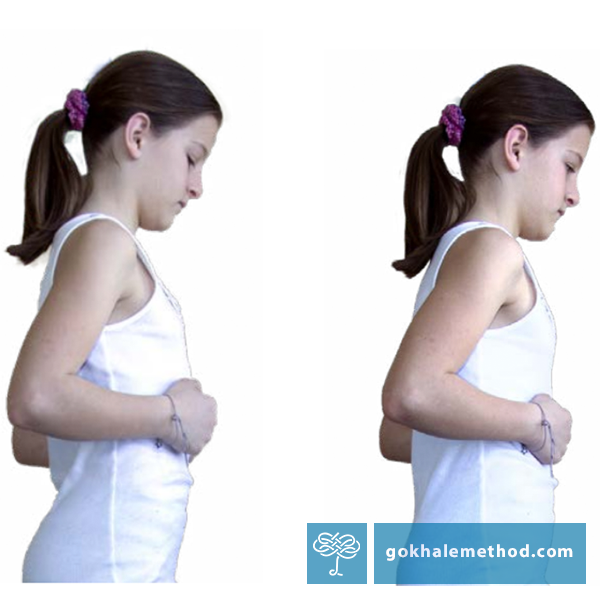
Align Your Rib Cage and Solve Your Back Tension
Choose your remedies carefully
There are many approaches to stretching tight back muscles that involve rounding the back. Though these exercises give temporary relief, we recommend against them because they threaten the spinal discs, nerves, and ligaments. They can also result in the back muscles contracting even more tightly to stabilize the area.
Ronald Katz’s Gokhale (Gō-clay) Method® Success Story
Before I settle in to recount my back pain story, let me fetch my Gokhale Pain-Free™Chair. This is the chair I now use for all my writing, and that’s important, as I am an author of mystery short stories, and spend many hours composing at my desk. Pain-free, I’m now glad to say.
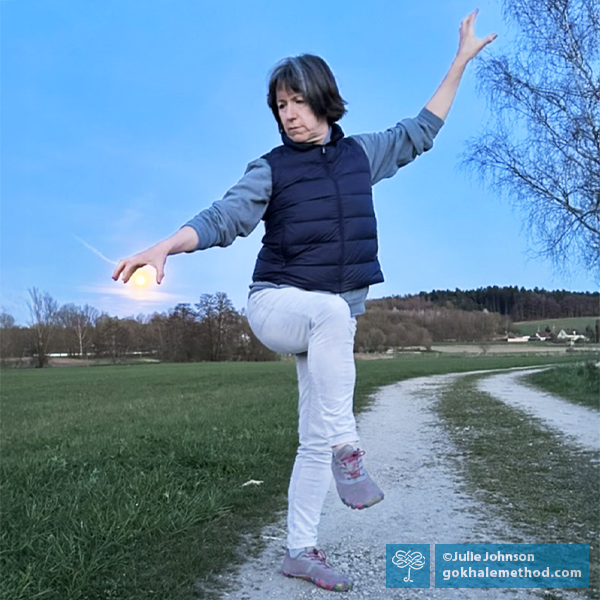
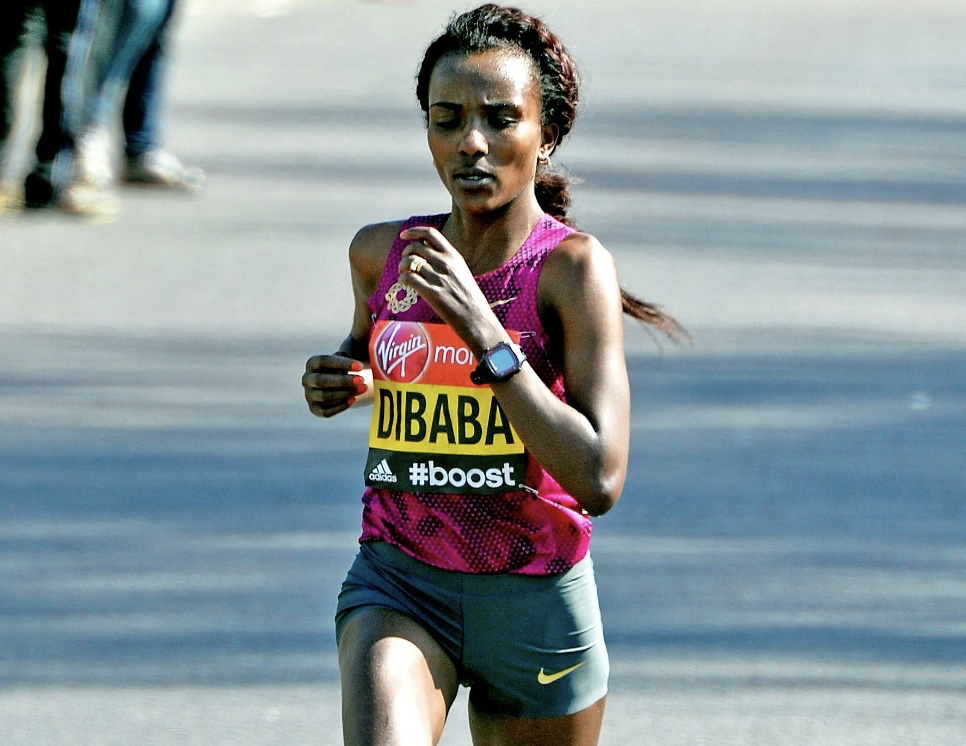
Gliderunning: Part 6: Upper Body
Welcome to the sixth blog post in our series on running. My name is Michelle Ball, and I am a Gokhale Method® teacher living in Tasmania. I am also a lifelong runner and am passionate about sharing the benefits of healthy posture with the running community, be that beginners, seasoned runners, or anyone in between. Even if you walk rather than run, the posture principles outlined in this post can still help you to enjoy an active and pain-free body well into old age.
Running with a well-positioned upper body
In this post we will consider the upper body. Runners are inclined to pay far less attention to the upper half of the body than the lower half, as they focus on gait pattern, cadence, footwork, and propulsion. This is hardly surprising, but the lower body, while super-busy, really is just half the story.
Healthy posture in the upper body brings the following benefits:
Protected spinal structures
Improved biomechanics
Unimpeded flow and momentum
Support that makes the body feel lighter
Athletic appearance