People often come to the Gokhale Method® when they suddenly can’t enjoy what they love to do. Their days playing golf, sailing, dancing, hiking, or simply playing with their children or grandchildren, are threatened. Life becomes an obstacle course of injuries, pain, and rehab. Their body is no longer a comfortable home where they feel good and self-confident.
Why Healthy Glutes Reduce Aches and Pains
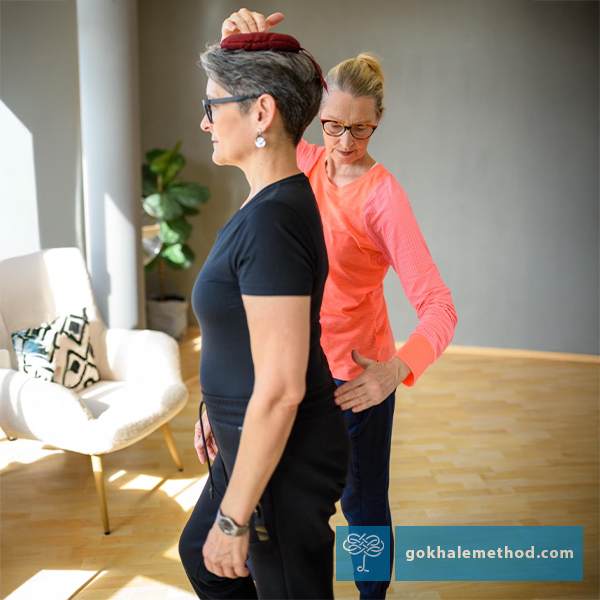
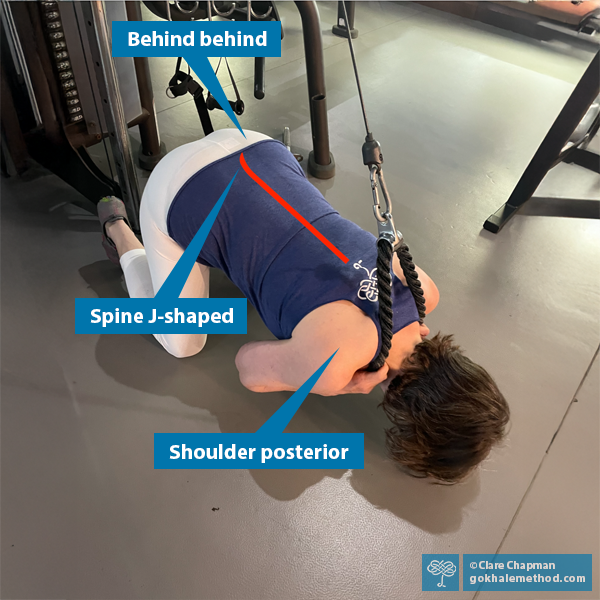
Over the decades that our students have gotten out of pain by learning the Gokhale Method®, it has become clear that healthy glutes are essential in this. Well-functioning glutes hold the key to unlocking many poor postural habits, and contribute to better biomechanics and movement. Good glute function will often solve pain and enable healing in apparently unconnected areas of the body. Let’s take a look at some of the common, and sometimes surprising, aches and pains that respond to our glute training…
Wake Up Your Glutes, They Snooze, You Lose
In surveys of what people find physically attractive in a partner, a shapely butt is often highly rated. Perhaps it’s no surprise, but if you want, there are even apps to help! So, are good-looking glutes all about sex appeal and filling out our clothing in a flattering fashion? While these concerns may be valid, it is also true that well-toned glutes have many other, profound, but less widely recognized attributes.
This blog post takes a look at the bigger picture of glute function. You may be surprised to find out just how much your glutes can contribute to healthy posture and a pain-free body.
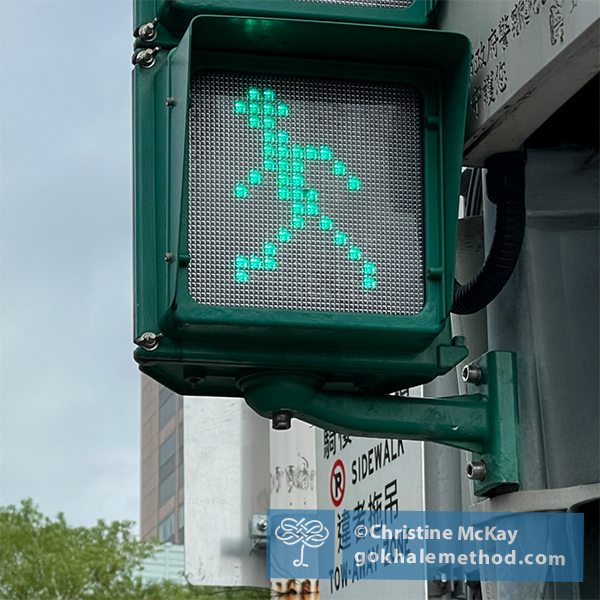
Give Your Walk the Green Light!
The best art often communicates on many levels. The Walking Men 99™ exhibit is a great example. It consisted of a frieze of pedestrian crossing icons, photographed and assembled from around the world. At human scale, they mingled with passersby on the sidewalk.
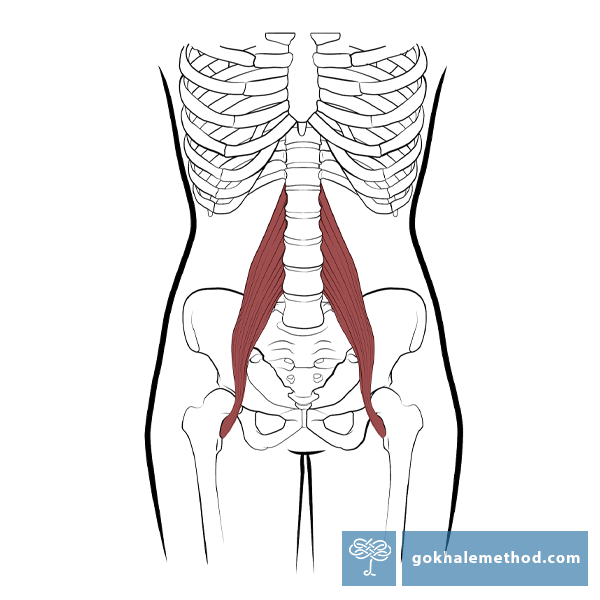
How to Fix a Tight Psoas
When students first meet with a Gokhale Method® teacher they are sometimes surprised to learn that one of the reasons for their back pain is a tight psoas muscle. What does this little-known muscle, embedded deep within our bodies, have to do with back pain? And what do we need to do to have it recede in the background and leave our backs alone?
How to Climb Stairs Part 1: Onward and Upward
Few of us, wheelchair users excepted, pass a day without climbing steps or stairs. Students often ask if posture has any bearing on how best to do this—and the answer is yes! Our approach to pain-free, healthy posture works precisely because it helps you with all your daily activities. This blog post is the first of several containing introductory tips for using steps and stairs. We will focus here on how to power yourself upward.
Steps and stairs—the benefits
If you are looking to maintain or improve your cardio fitness and lower body strength, climbing steps and stairs will check that box. For example, this could be opting for the stairs rather than the elevator at work.
Glidewalking: Sitting’s Long-Lost Counterpart
Mother and son in a tribal Orissan village demonstrating excellent walking form. Notice that their heels remain on the floor well into their stride.
Do you have tight psoas muscles? Do you suspect the cause is too much time spent sitting in your daily life? There’s a complementary activity that helps counterbalance the time we spend sitting: walking — or, more specifically, glidewalking. Glidewalking helps balance our sitting in numerous ways — walking is dynamic versus sitting which is static. Yang balances Yin, viewed in the framework of traditional Chinese medicine. One underappreciated way in which walking can balance sitting pertains to the psoas muscle.
The psoas muscle originates on