It’s early January. New Year’s resolutions are swinging into action, and many of them involve improving our health. With the impetus of a fresh start we throw ourselves into ditching poor habits and cultivating better ones. It’s no surprise that January sees the highest gym sign-ups and enrollments for dietary regimens! Other resolutions include getting more sleep, meditating, or learning a new skill—self-care for the mind as well as the body.
Family Cycling: That’s How We Roll
Cycling has been a passionate sport and hobby of mine for decades. I am no longer a professional bike racer; I am now a mother and Gokhale Method® teacher. As a result, I have become more observant of what can “go wrong”, posturally speaking, when riding a bicycle. And I work to improve my posture as I pedal. For example, it takes vigilance to keep my shoulders back and my head aligned with my torso. I now know how cycling can enhance my form, and vice versa. I also enjoy modeling key posture principles to guide my daughters and partner so that they too can be comfortable and healthy on a bicycle.
Cycling is a part of family life
In this blog post I would like to share with you some of the cycling activities and posture tips that have benefitted us as a family. Prior to parenthood, my partner and I raced and trained together for many years, traveling to quite a few states and even abroad to indulge our passion. When our daughters were born we decided that, at least in our busy city, Somerville, MA (the most densely-populated city on the Eastern Seaboard, USA!), we would get about with them on bicycles instead of driving.
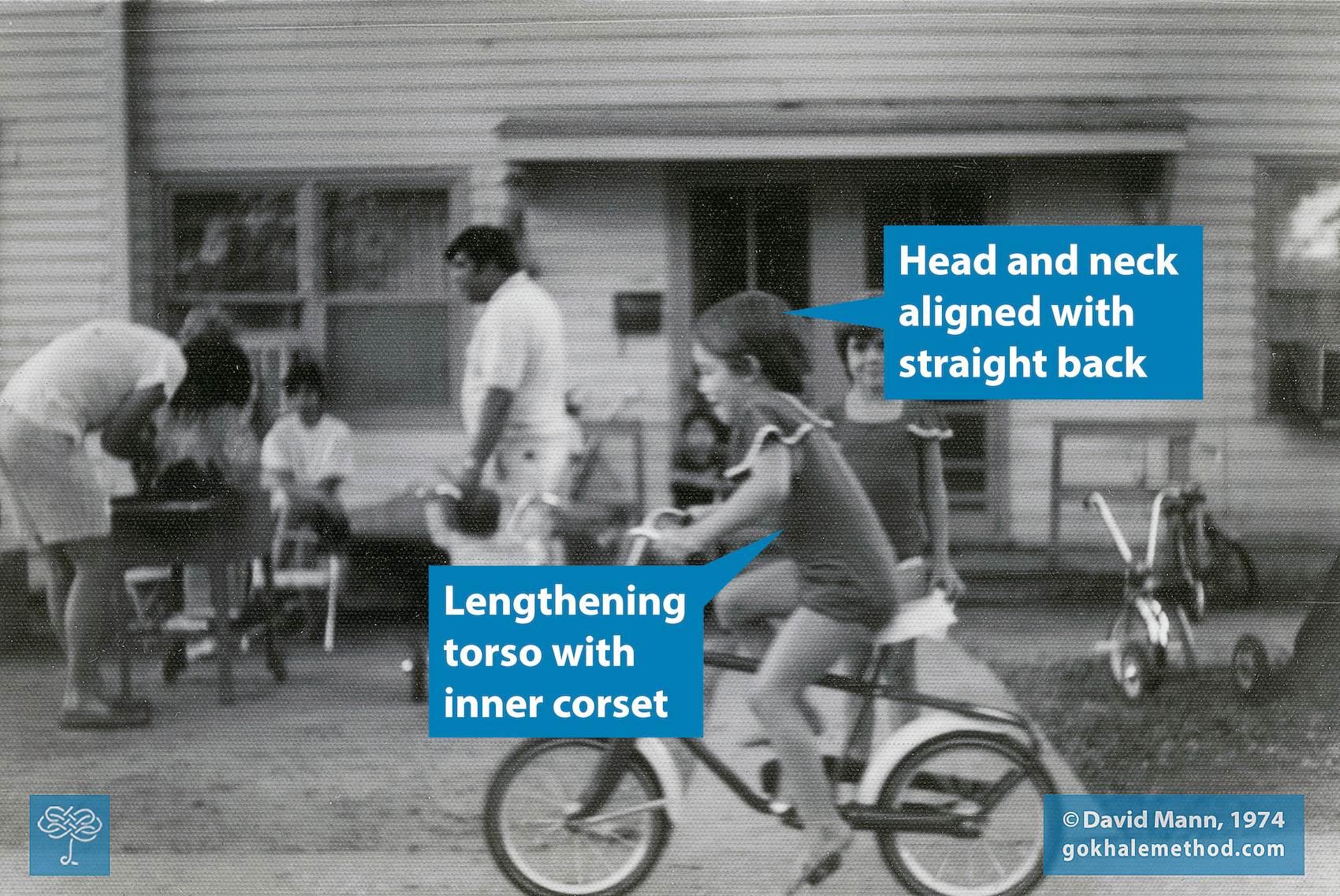
Five Posture Tips to Power Your Cycling
This is Part 3 of a three-post series on cycling with healthy posture by Gokhale Method teacher and longtime cyclist Tiffany Mann. Read Part 1 and Part 2 here.
Spring has arrived, and perhaps like many people, you want to spend more time on your bike! Maybe you’re already an avid cyclist looking for some tips to make cycling more comfortable and sustainable for years to come; or you’ve taken a break and are ready to step back on the pedals. Perhaps you just want to get up those hills!
Even if you are a beginner, it is so satisfying and pleasurable to use your own muscle power to propel yourself on this simple machine; but it is still well worth looking at how to use your energy as economically as possible. Cycling doesn’t have to be superhard work, and you can benefit your posture at the same time.
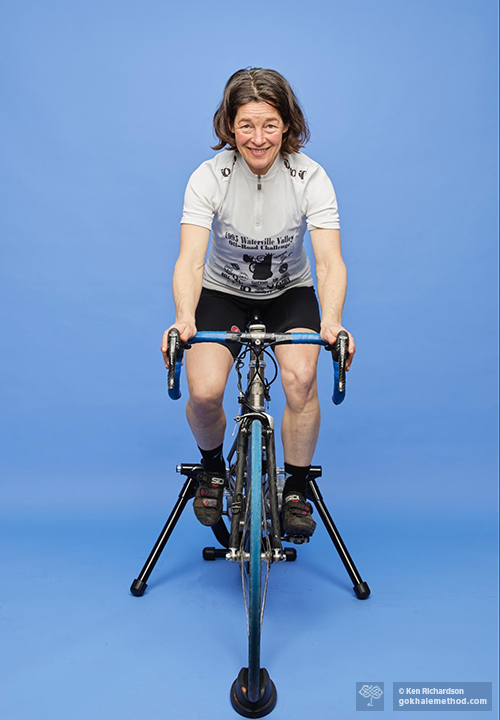
How to Beat Neck and Shoulder Pain While Cycling (Cycling for Everyone, Part 2)
Neck and/or shoulder pain is a common ailment even experienced cyclists regularly encounter, but posture can help! It takes awareness and muscular engagement while cycling to not allow gravity to further pull the head forward and down and round or hunch the shoulders, a posture problem that is already prevalent in our modern culture. However, the payoff is worth it! You will be able to ride pain-free for longer, and will also be patterning a healthy upper body position regardless of your activities and movements. You will also strengthen and develop baseline tone in stabilizing muscles, and they will become more accustomed to doing the job of maintaining shoulders back, back of the neck tall and straight, and head lined up over the body.
Why Cycling is the Perfect Posture-Friendly Exercise for the COVID Era
I’m a longtime cyclist, former elite-level mountain bike racer, and Gokhale Method teacher. Learning and applying Gokhale Method techniques helped me reduce lumbar strain caused by unhelpful posture habits I used to employ while riding. I continue riding to this day, along with my whole family — now free of lower back pain. In my humble opinion, bikes are the most perfect exercise equipment of all time. This is especially true for the COVID era! The wheel base between two bicycles is around 6 feet, so riding with others can be done safely. Add Gokhale Method techniques to the mix, and you’ve got a recipe for full-body health.