Hypermobility
Flexibility in the body is generally regarded as a plus, and most people want more of it. Flexibility is seen to enable a wide range of motion, avoid muscle pulls, and spare wear and tear in overly tight joints. But like most things in life, you can have too much of a good thing. In this blog post we are going to look at why excessive mobility has a downside and how healthy posture can mitigate that.
An exceptional range of motion makes for a very “bendy” looking body. Enter the age-old art of the contortionist, a mainstay of acrobatic troupes, circuses, and fairs, which for centuries have enthralled and appalled audiences in equal measure.
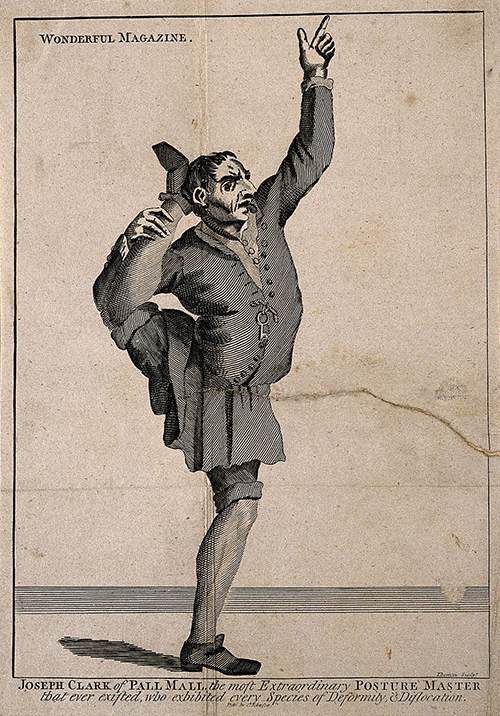

“The most Extraordinary Posture Master.” Wikimedia
Engraving of Joseph Clark of Pall Mall, London, England, by Thornton, c. 1690
What is hypermobility?
An unusual degree of flexibility is still sometimes referred to as being “double-jointed,” but this is poetic license and inaccurate—hypermobility is a better term. Hypermobility is usually due to laxity in the ligaments that holds one bone to another, forming the joint. Hypermobility enables more rotational movement in ball and socket joints such as the hip, more “bend” at hinge joints like the knee and elbow, and also larger angles of bend between the vertebrae of the spine. Hypermobility can be genetic, acquired by persistent over-stretching, or a combination of both.
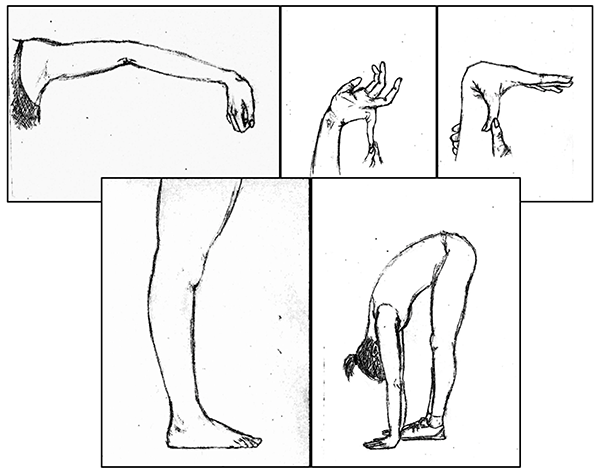
The Beighton score, along with other criteria, is used to assess hypermobility. It gives 1 point for each elbow and knee that hyperextends by 10 degrees or more (4 points), 1 for each little finger that bends back by 90 degrees (2 points), 1 for each thumb which can be touched to the forearm (2 points), and 1 for touching the floor with the palms. Wikimedia
Hypermobility can do damage
Unfortunately, there is a high incidence of injury associated with over-stretching ligaments, which lack abundant blood supply to repair themselves and the elasticity to return to their baseline length. Most professional dancers, gymnasts, or acrobats are trained from an early age to further enhance their natural flexibility with stretching regimens. But this can be taken too far.
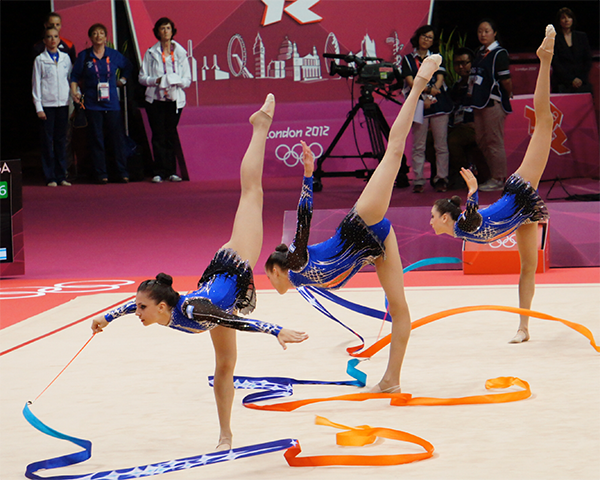
Israeli rhythmic gymnasts at the 2012 London Olympics. Note the hyperextension of the center gymnast’s standing leg,
which bows backward. Wikimedia
A memorable example of taking flexibility and stretching to the point of damage was the career of gymnastics champion Olga Korbut. Having won gold at the 1972 Olympics she toured West Germany. In her autobiography she wrote, “During that tour of Germany, the lumbago in my back began to hurt more and more. The Novocaine injections took away the pain for a while, but I needed time to rest and heal. By the end of the tour, I walked as though I had a stake in my spine.”
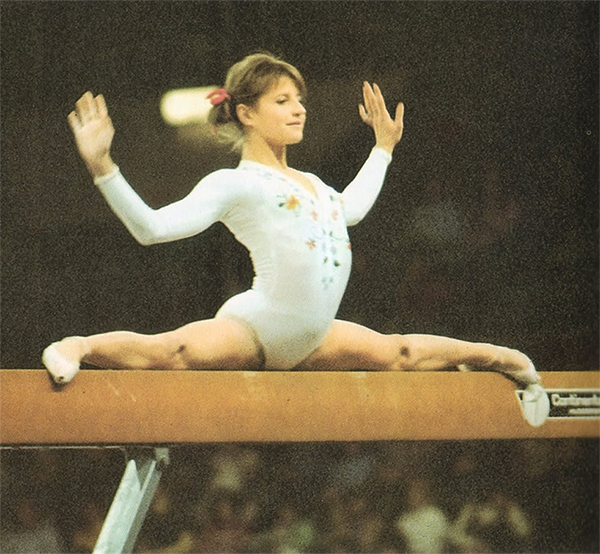

Olga Korbut demonstrating her prowess on the beam. Her upper lumbar spine is being pushed into significant curves. Alchetron
Protecting the spine
It is common to find vertebrae that have become hypermobile where the adjacent section of spine has become stiff and lacks movement. This can be a particular issue in movements such as a golf swing, where it is important that the rotation be distributed appropriately through the whole body rather than achieved by an extreme twist between a few vertebrae.
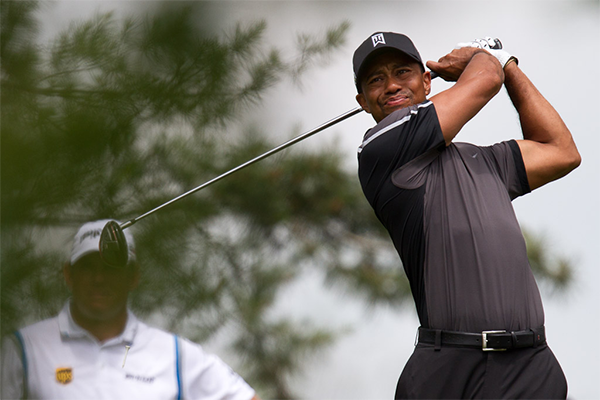

Tiger Woods follows through with rotation throughout his body, not just twisting at the waist. Flickr
Hypermobility in the spine can result in damage to all its structures. The vertebrae may lay down problematic extra bone in an effort to protect the area. The discs are also at risk of wear and tear and herniation, and the nerves risk compression. Muscles may become hypertonic (held tight) or spasm in an effort to stabilize the area and protect the delicate structures of the spine.
If you do have a genetic disposition to hypermobility, then it’s important to have adequate strength in the muscles surrounding the affected joints to maintain good alignment. Equally important knowledge of healthy posture will ensure you know how to find and keep ideal alignment.
Protecting elbows and knees
If you have hypermobile elbows and are on all fours, don’t “park” into those joints. You want to retain a little “give” at the elbow creases. This works the muscles around the elbow joints, affording them protection and encouraging the hands to also be responsive rather than compressing the wrist joints as they take all the weight.
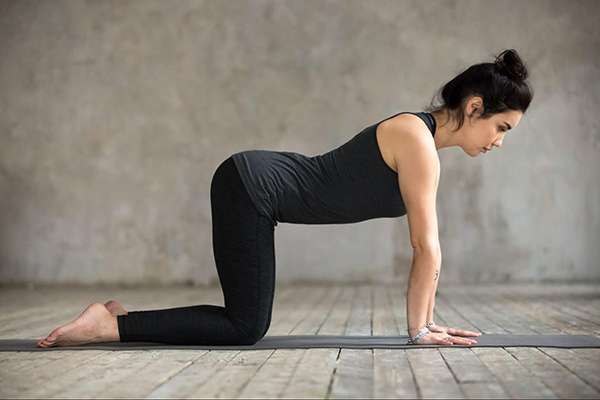

Avoid locking out your elbows, which pushes into the joints and further distends their ligaments. In the example above, the hands are inactive and all the weight is pressed into the wrist joints. Freepik
Similarly, if you have hypermobile knees, you don’t want your knees to go past straight to bow backward when standing. If this is a habit for you, join me on the 1-2-3 Move program on Monday, September 6 and I will show you a couple of dance techniques to displace this habit. You can also join Eric for Gokhale Fitness on Tuesday, September 7 when he will share an exercise approach to maintaining healthy knee joints.
If you would like to join either or both of these classes but have not yet subscribed to the 1-2-3 program, sign up now for your 7-day Gokhale Exercise Free Trial.

1-2-3 Move happens daily with Esther or guest teachers at 9:45 a.m. (Pacific Time)
Gokhale Fitness with Eric runs Mondays, Wednesdays, Fridays from 7–7:25 a.m.
(Pacific Time), and Tuesdays, Thursdays, Saturdays from 3–3:25 p.m. (Pacific Time)
Gokhale Moving Meditation with Roberta is Mondays at 2 p.m. and with Kathleen is Wednesdays at 12 p.m. (Pacific Time)
Flexibility in your body is a wonderful thing. It looks good, and feels good, but requires some wisdom in its usage. The Gokhale Method® approach to movement and exercise is always holistic, supports good posture habits, and develops the necessary strength to protect the joints from injury.
If you would like an expert one-on-one assessment of your posture and flexibility you can arrange an Online Initial Consultation or take an in-person Initial Consultation if you have a Gokhale Method Teacher near you.

Comments
Thank you so much, Esther,
Thank you so much, Esther, for this blog. Have sent it to my Ehlers-Danlos friends and also posted on our local EDS Facebook page. Looking forward to the classes!
Hi Gomati, We've had a number
Hi Gomati, We've had a number of students over the years who have EDS and have reported our simple techniques to be life-changing. So glad you are helping more people hear about this approach!
Another interesting article
Another interesting article Esther, thank you. Although I am not hypermobile in any way (obviously a good thing!); it is good to know these types of movements typcially touted as very "cool" are not so much. Looking at the photo of Olga Korbut made me cringe .... this pose is so far from the natural way a body is supposed to be in movement and flexibility ... I think we all need to be hyper "aware" vs. hyper "mobile" when it comes to the everyday functioning of our bodies. Thank you for posting this insightful article :)
Hyperaware is good!
Hyperaware is good!
Add New Comment
Login to add commment
Login