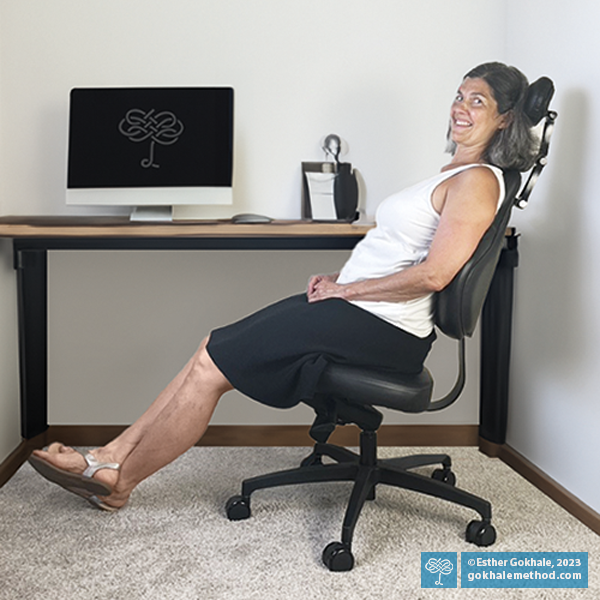
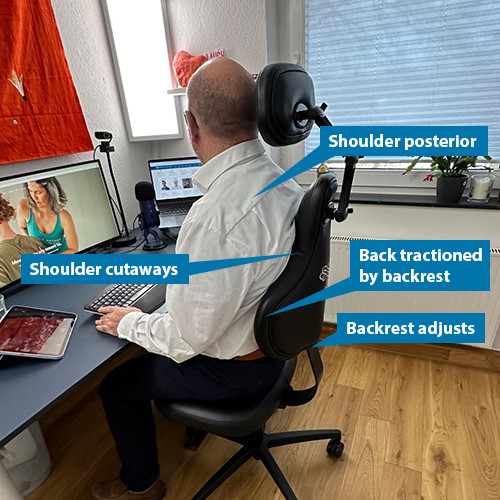
There’s no doubt that dysfunction abounds when it comes to sitting. Most of us spend many hours on poorly designed chairs, in poor posture. As many people know all too well, poor sitting habits can definitely set you up for chronic back pain and tension.
The good news? With just a little time and awareness, we can learn to sit well. There is real beauty and functionality in sitting done skilfully! When you do, sitting becomes not only comfortable, but also healthful and therapeutic.
Biotensegrity—Another Way to Understand Your Body
In our culture a loss of up to 50% of the height of the discs as we age from our twenties to our fifties is considered normal. It follows that the herniations, nerve pain, and arthritic change that accompanies this chronic degeneration of our discs is also not seen as unusual. Pain and reduced ability to function is normalized.
Recline and Relax, Executive-style!
Over the years, I have often shown students with recliners that they can get a compression-relieving stretch in their lower back as the backrest slides away from the seat (assuming the mechanism is designed advantageously). This is something you might like to try out for yourself.
The Gokhale® Wedge 2.0
In Spring last year we launched the Gokhale® Wedge. For years, our students have been requesting a convenient, ready-made wedge for upright sitting without a backrest, one that doesn’t require folding blankets and other makeshift (pun intended) measures. The requests also specified an attractive item to enjoy around the home or office, and that it be of durable quality, keeping its shape and good looks with daily use.
Clare’s Gokhale Method® Success Story
In January and February this year I took the Gokhale Method Elements course, which consists of 18 brief (13 minute) but potent lessons. I would like to share my experience of the Gokhale Method with you in this blog post.
My goals were to find out how to sit, stand, and walk well, so that I don’t overstress the scoliotic parts of my back. I was also in search of more comfortable and beneficial sleeping positions. I felt I needed guidance to help me develop a better sense of my body posture and alignment. To be able to do a one-on-one course online made this possible for me.
It was only when I saw the difference between my “Before” and “After” pictures that I realized just how much change it was possible to make to my posture in such a relatively short period.
How Do I Fix My Neck Pain?
Do you suffer from neck tension, muscle knots, or tingling in your fingers? Do you get frequent headaches?
Or maybe your neck is fine most of the time, but seizes up periodically, leaving you unable to function normally in your job, family life, and recreational activities.
Most neck pain involves compression.
In modern cultures, the head often drifts forward as we slouch and crane our necks towards our computer screens. The weight of the head, (typically 11 lb. or 5 kg—think bowling ball), then requires the muscles at the back of the neck to contract strongly to keep the head up. This contraction compresses the relatively delicate tissues in the area. Not a recipe for a healthy, happy neck. If you have forward head carriage but are symptom-free so far, keep reading for tips that will prevent future problems with the discs, nerves, blood vessels, and bones in your neck.
Ronald Katz’s Gokhale (Gō-clay) Method® Success Story
Before I settle in to recount my back pain story, let me fetch my Gokhale Pain-Free™Chair. This is the chair I now use for all my writing, and that’s important, as I am an author of mystery short stories, and spend many hours composing at my desk. Pain-free, I’m now glad to say.
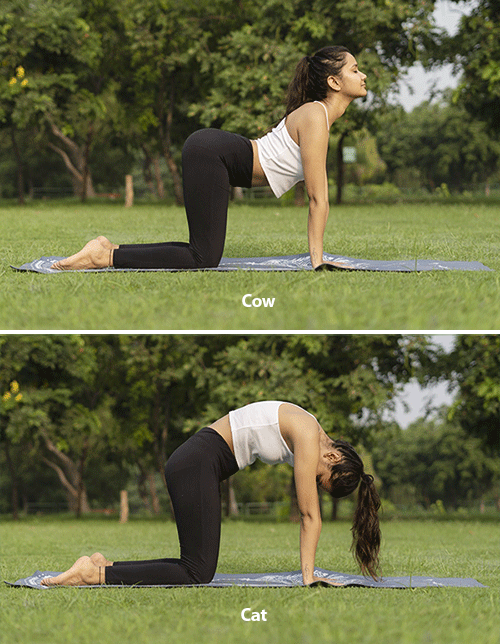
Home Exercises Part 3: Cat-Cow
This is our third blog post in the series where we put popular exercises under scrutiny to examine how they stack up—or not—against the principles of healthy posture. Here we are looking at “Cat-Cow,” a common exercise for mobilizing the spine.
Cow is one of the “holy cows” of conventional exercise. Done on all fours, it puts the spine into extension (swaying). It is paired with Cat , which puts the spine into flexion (rounding). Alternating between these postures is widely considered to be a good or even necessary exercise for mobilizing the spine.
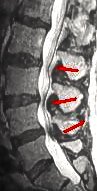
Epidural steroid injections for lumbar spinal stenosis?
A four-year study involving 276 spine patients ages 53 to 75 published in the journal Spine suggests that we should--at the very least--take a deep breath and think twice before choosing epidural steroid injections to relieve the pain of lumbar spinal stenosis, not only because this oft-used treatment may not work, but also because it may cause more harm than good. Better yet and instead it might make sense to simply get in the habit of breathing deeply, which naturally lengthens the spine and helps relieve unhealthy stress on the vertebrae... But more about Gokhale Method solutions in just a bit!