Outer Corsets and Inner Corsets
Home Exercises Part 2: Crunches
This is our second blog post in the series where we put popular exercises under scrutiny to examine how they stack up—or not—against the principles of healthy posture. Here we are looking at crunches, a common abdominal exercise.
Crunches are often seen as a better targeted and safer
abdominal exercise than sit-ups—but there is still a downside.
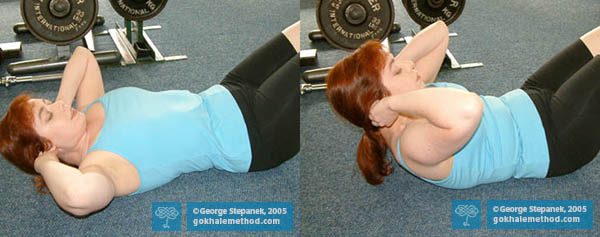
Crunches are done lying down on the floor, face up, knees bent with feet on the floor, and with the hands placed behind or to the side of the head. They involve using the muscles of the rectus abdominis and the obliques to repeatedly raise and lower the upper body.
Crunches are well named—they crunch your discs and crunch your nerves. Lifting the
What is the Best Ab Exercise?
The abdominal crunch, though ubiquitous, is actually quite detrimental to the spinal discs and nerves. Better to find an abdominal exercise which respects and protects the spine! Image courtesy Jonathan Borba on Unsplash.
Happy Holidays! The dawning of a new year is a time when many people make efforts to establish new habits, many of them body-related. With the desire to improve ourselves often comes a (sometimes unhealthy) heightened awareness of how our bodies and their shapes appear to others. This is particularly true of abdominal muscles. Photoshopped, unrealistic images of sculpted torsos plaster newsstand covers every January. Crunches are the most commonly recommended exercise for
Forward Pelvis: the Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
Opinions on what constitutes a pelvic problem abound. The term "forward pelvis" with its negative connotation, has come to be used for an assortment of pelvic / lumbar architectures, some of which, according to the Gokhale Method - are good, and some bad.
Have you been diagnosed with “forward pelvis” (aka “anterior pelvic tilt”)? If so, you may be concerned about the Gokhale Method recommendation to antevert your pelvis, thinking that this will exacerbate the problem.
Your confusion is not unique. Very few professionals, whether doctors, trainers, or wellness practitioners, differentiate between “forward pelvis / anterior pelvic tilt” and healthy pelvic anteversion. This can lead to poor